I/O流,输入/输出流。数据在设备间的传输称为流,IO流就是用来处理设备间数据传输问题的。
常见应用场景(文件复制,文件上传,文件下载)
Java中流分为字节流和字符流,又细分为字节输入流(Reader),字节输出流(Writer),字符输入流(InputStream),字符输出流(OutputStream)
字节流
字节流抽象基类:
InputStream:这个抽象类是表示字节输入流所有类的超类(读数据)
OutputStream:这个抽象类是表示字节输出流所有类的超类(写数据)
FileOutputStream
构造方法
FileOutputStream(String name) 创建文件输出流以指定的名称写入文件, 用于写入诸如图像数据之类的原始字节的流
FileOutputStream(File file) 创建文件输出流以指定的文件对象写入文件File file = new File("src");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
等价于
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("src"))
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建字节输出流对象: 1、调用系统api创建了文件 2、创建字节输出流对象 3、让字节输出流对象指向创建好的文件
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("/Users/b/Desktop/java1.txt");
// void write(int b)
// 将指定字节写入此文件输出流。
fileOutputStream.write(97); //根据ascii表对应字符
fileOutputStream.close(); //1、释放相关资源,2、关闭此输出流
}字节输出流写数据的三种方式
void write(byte[] b) 将 b.length 个字节从指定 byte 数组写入此文件输出流中。
void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) 将指定 byte 数组中从偏移量 off 开始的 len 个字节写入此文件输出流。
void write(int b) 将指定字节写入此文件输出流。
public class FileOutputStreamDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("/Users/b/Desktop/java1.txt");
// void write(int b) 将指定字节写入此文件输出流。
fileOutputStream.write(97);
fileOutputStream.write(98);
fileOutputStream.write(99);
fileOutputStream.write(100);
fileOutputStream.write(101);
//void write(byte[] b) 将 b.length 个字节从指定 byte 数组写入此文件输出流中。
byte[] b = {102, 103, 104, 105, 106}; // f g h i j
fileOutputStream.write(b);
//void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) 将指定 byte 数组中从偏移量 off 开始的 len 个字节写入此文件输出流。
byte[] c = {107, 108, 109, 110, 111}; //k l m n o
fileOutputStream.write(c, 1, 3); //这里偏移量为1,即跳过k,从l开始写,len为3,即写入3个字节也就是lmn 没有 o
}
}String <=> Byte
String str = "string";
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
for (int b1 : bytes
) {
System.out.println(b1);
}追加写入
public FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append) throws FileNotFoundException创建一个向具有指定 name 的文件中写入数据的输出文件流。如果第二个参数为 true,则将字节写入文件末尾处,而不是写入文件开始处。
FileOutputStream fos1 = new FileOutputStream("/Users/b/Desktop/java1.txt", true);
//append:true ,此时为追加写入的字节输出流
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("/Users/b/Desktop/java1.txt");
FileOutputStream fos1 = new FileOutputStream("/Users/b/Desktop/java1.txt", true);
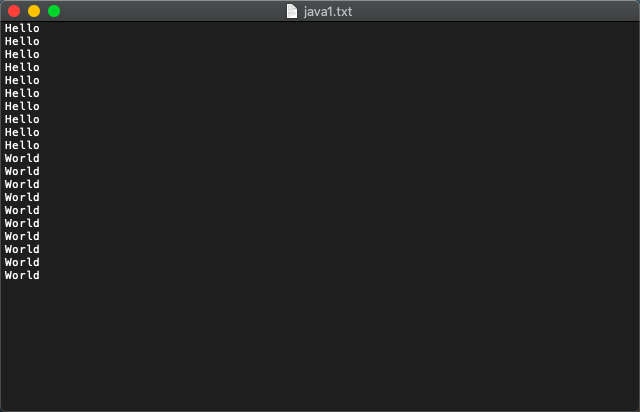
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
fileOutputStream.write("Hello".getBytes());
fileOutputStream.write("\n".getBytes());
}
fileOutputStream.close();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
fos1.write("World".getBytes());
fos1.write("\r".getBytes());
}
fos1.close();
}
异常捕获
public class FileOutpuStreamExcept {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fos = new FileOutputStream("/Users/b/Desktop/java1.txt");
fos.write("Exception".getBytes());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}readFile&writeFile
import java.io.*;
public class ByteStreamTestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteStreamTestDemo bstd = new ByteStreamTestDemo();
String inputstr = bstd.readFile("/Users/b/Desktop/image1.txt");
System.out.println(inputstr);
bstd.writeFile("/Users/b/Desktop/image1.txt", "Hello Java");
}
public String readFile(String path) {
FileInputStream fis = null;// 实例化FileInputStream对象;
String str = null;
try {
// 1.根据path路径实例化一个输入流的对象
fis = new FileInputStream(path);
//2. 返回这个输入流中可以被读的剩下的bytes字节的估计值;
int size = fis.available();
//3. 根据输入流中的字节数创建byte数组;
byte[] array = new byte[size];
fis.read(array);//4.把数据读取到数组中;
//5.根据获取到的Byte数组新建一个字符串,然后输出;
str = new String(array);
System.out.println(str);//输出;
} catch( FileNotFoundException e) {
// 解决new FileInputStream(path);可能会发生的异常;
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// 解决fis.available()时可能发生的异常;
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//6.在最后,关闭我们的IO流
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return str;
}
public void writeFile(String path, String content) {
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
//1.根据文件路径创建输出流
fos = new FileOutputStream(path);
//2.把string转换为byte数组;
byte[] array = content.getBytes();
//3.把byte数组输出;
fos.write(array);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// 解决new FileOutputStream(path)出现的问题
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// 解决fos.write(array)可能会出现的问题;
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
/*
* 在方法的最后一定实现这个方法;
*/
try {//4.关闭IO流
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}FileInputStream

FileInputStream.read()
intread() 从此输入流中读取一个数据字节。 intread(byte[] b)从此输入流中将最多b.length个字节的数据读入一个 byte 数组中。intread(byte[] b, int off, int len)从此输入流中将最多len个字节的数据读入一个 byte 数组中。
FileInputStream.read()
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建读数据对象
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("/Users/b/Desktop/java1.txt");
//读取对象
int read = fis.read();
while(read != -1) {
System.out.println(read);
System.out.println((char)read);
read = fis.read();
}
//释放资源
fis.close();
}
int by;
while((by = fis.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char)read);
}复制字符流文件
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("/Users/b/Desktop/java1.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("/Users/b/Desktop/java2.txt");
int by;
while ((by = fis.read()) != -1) {
fos.write((char)by);
}
fis.close();
fos.close();
}复制Byte流文件
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("/Users/b/Desktop/Images/image-2.png");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("/Users/b/Desktop/image1.png");
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = fis.read(b)) != -1){
fos.write(b);
}
fis.close();
fos.close();
}读取内容方法
int read() 从此输入流中读取一个数据字节。 int read(byte[] b) 从此输入流中将最多 b.length 个字节的数据读入一个 byte 数组中。 int read(byte[] b, int off, int len) 从此输入流中将最多 len 个字节的数据读入一个 byte 数组中。 参数为内容存入的byte数组,返回值为该数组的长度或者说数据元素的个数,如果已到达文件末尾,则返回 -1。
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("/Users/b/Desktop/java2.txt");
byte[] bys = new byte[1024];// 这里通常放1024及其整数倍的数据
int len;
while((len = fis.read(bys)) != -1){
System.out.println(len);
System.out.print(new String(bys, 0, len));
}
fis.close();
}String <=> Byte 编码转换
String -> Byte byte[] getBytes() 使用默认字符集将String转换为Byte存储在数组内 byte[] getBytes(String charsetName) 使用指定的字符集将该String编码为Byte存储在数组内
Byte -> String String(byte[] bytes) 使用默认字符集将Byte转换为String String(byte[] bytes, String CharsetName) 使用指定字符集将Byte转换为String
public static void main(String[] args) {
//String => Byte,默认UTF-8
String s = "zh1z3ven";
byte[] bytes = s.getBytes();
System.out.println(bytes);
for (int i : bytes
) {
System.out.println(i);
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes));
//Byte => String
byte[] b = {97, 98, 99, 100, 101, 102};
String str = new String(b);
System.out.println(str);
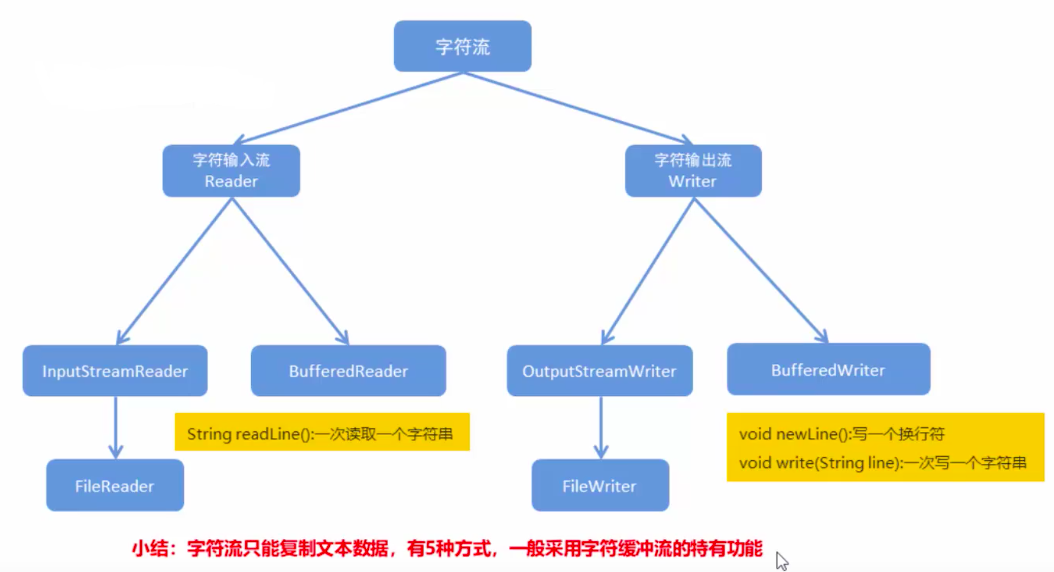
}字符流
字符流抽象基类
字符流处理的是字符数据,而字节流处理的是byte数据
Witer 字符输出流抽象基类
Reader 字符输入流抽象基类
对应的子类为
OutputStreamWriter 使用指定的Charset将字符编码为字节,从字符流到字节流的桥梁
InputStreamReader 读取字节,用指定的Charset将字节编码为字符,从字节流到字符流的桥梁
这两个类的优点就是可以处理不同字符集的流
如果都是默认字符集或者字符集一样的话可以使用 FileReader和FileWriter
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File f = new File("/Users/b/Desktop/image1.txt");
f.createNewFile();
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(f);
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos);
osw.write("zh1z3ven");
osw.close();
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(f);
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);
int len;
while ((len = isr.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println(len);
System.out.println((char)len);
}
isr.close();
}OutputStreamWriter
void write(int c) 写入一个字符 void write(char[] cbuf) 写入一个字符数组 void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) 写入一个根据cbuf,以off为偏移量,长度为len的字符数组的一部分 void write(String str) 写入一个字符串 void write(String str, int off, int len) 写入字符串的一部分
void write()
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("/Users/b/Desktop/image1.txt"));
osw.write(97);
char[] cbuf = {'c', 'v', 'b', 'n', 'm'};
osw.write(cbuf);
osw.write(cbuf, 1, 4);
String str = "zh1z3ven";
osw.write(str);
osw.write(str, 2, 3);
osw.flush();
osw.close();
}InputStreamReader
int read() 一次读一个字符,返回字符对应的ascii值
int read(char[] buf) 一次读一个字符数组
int read()
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("/Users/b/Desktop/image1.txt"));
//int read() 读取文件
int ch;
while ((ch = isr.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char)ch);
}
isr.close();
}int read(char[] buf)
public class InputStreamReaderDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("/Users/b/Desktop/image1.txt"));
//int read(char[] buf) 读取文件
char[] ch = new char[1024]; //以char数组接受文件内容
int len; //存储char数组长度
while((len = isr.read(ch)) != -1){
String str = new String(ch, 0, len); //将char转为String
System.out.print(str);
}
isr.close();
}
}字符流复制文件
最明显的一点就是不需要再进行Byte<=>String的转换了
0x01 一次读写一个数据
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("/Users/b/Desktop/java2.txt");
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("/Users/b/Desktop/java4.txt");
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos);
int ch;
while((ch = isr.read()) != -1){
osw.write(ch);
}
}0x02 一次读取一个字符数组
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//OutpuStreamWriter.write(String str) + InputStreamReader().read()
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("/Users/b/Desktop/java2.txt");
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);
char[] chars = new char[1024];
isr.read(chars);
String str = new String(chars);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("/Users/b/Desktop/java3.txt");
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos);
// String str = "琥珀色黄昏像风在很美的远方" + "\n" + "你的脸没有化妆我却疯狂爱上";
osw.write(str);
System.out.println(str);
isr.close();
osw.close();
}FileReader
用于读取字符文件的便捷类
继承自InputStreamReader类,即可一次读一个字符或一次读一个字符数组
FileReader(String fileName)FileWriter
用于写入字符文件的便捷类
继承自OutputWriter类
FileWriter(String fileName)FileReader&FileWriter读写复制文件
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader("/Users/b/Desktop/java2.txt");
FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter("/Users/b/Desktop/java6.txt");
char[] chars = new char[1024];
int len;
while((len = fileReader.read(chars)) != -1){
fileWriter.write(chars, 0 ,len);
}
fileReader.close();
fileWriter.close();
}可以简单理解为简化了InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter新建字符流对象的过程。
但是不可以处理不同字符集的数据流。
字符缓冲流
BufferedReader
从字符输入流中读取文本,缓冲各个字符,从而实现字符、数组和行的高效读取。
可以指定缓冲区的大小,或者可使用默认的大小。大多数情况下,默认值就足够大了。
主要用到的还是read方法
int read(char c) int read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) String readLine() 读取一个文本行
BufferedWriter
将文本写入字符输出流,缓冲各个字符,从而提供单个字符、数组和字符串的高效写入。
可以指定缓冲区的大小,或者接受默认的大小。在大多数情况下,默认值就足够大了。
主要用到的还是write方法
void newLine() 写入一个行分隔符。 void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) 写入字符数组的某一部分。 void write(int c) 写入单个字符。 void write(String s, int off, int len) 写入字符串的某一部分。
复制文件操作
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("/Users/b/Desktop/java2.txt"));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("/Users/b/Desktop/java7.txt"));
//一次读取一个字符
int ch;
while ((ch = br.read()) != -1){
bw.write((char) ch);
}
br.close();
bw.close();BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("/Users/b/Desktop/java2.txt"));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("/Users/b/Desktop/java7.txt"));
//一次读取一个字符数组
int len;
char[] chars = new char[1024];
while ((len = br.read(chars)) != -1){
bw.write(chars, 0 ,len);
}
bw.flush();
br.close();
bw.close();readLine()与newLine()
一般使用字节缓冲流一次读取一个字节数组的方式读取文件
void newLine() 写入一个行分隔符。自动根据系统而定
String readLine() 读取一个文本行(不包含换行符)。当读到null时,证明已读完此文件
write()
newLine()
flush()
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("/Users/b/Desktop/java2.txt"));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("/Users/b/Desktop/java8.txt"));
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(line);
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
br.close();
bw.close();
}标准输入流
InputStream
InputStream -> InputStreamReader -> BufferedReader
将标准输入流转换为字符缓冲输入流处理
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
获取一行键盘输入,是Scanner类的底层
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.print("请输入字符串:");
String line = br.readLine();
System.out.println("你输入的字符串是:" + line);
System.out.print("请输入一个整数:");
int len = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()); // 将字符串=>整型
System.out.println("你输入的数是:" + len);
}PrintStream
PrintStream ps = Systm.out
常见的方法有 println,print字节打印流

序列化与反序列化
对象序列化,就是将对象变成一个字节序列保存在磁盘或者在网络中传输对象。
对象反序列化,就是将序列化对象的字节序列进行反序列化重构对象。
序列化流:ObjectOutputStream
反序列化流:ObjectInputStream
ObjectOutputStream

void writeObject(OutputStream out)
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//构造方法: ObjectOutputStream(OutputStream out)
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("/Users/b/Desktop/java10.txt"));
Student zh1z3ven = new Student("zh1z3ven", 21);
//void wirteObject(Object obj);将指定对象(该对象需要implements Serializable)写入流中,最后保存在文件内
oos.writeObject(zh1z3ven);
//释放资源
oos.close();
}ObejctInputStream

public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//创建ObjectinputStream对象
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("/Users/b/Desktop/java10.txt"));
//readObject()反序列化
Object obj = ois.readObject();
//向下转型
Student s = (Student) obj;
System.out.println("Name: " + s.getName() + " Age: " + s.getAge());
//释放资源
ois.close();
}反序列化时可能存在的问题
1、假如我们在一个类序列化后去修改了它的类文件,在进行反序列化读取对象时可能会出现问题会抛出如下异常
java.io.InvalidClassException
因为类的串行版本与从流中读取出来的不一致而导致的
2、java强烈建议需要序列化的类 定义一个serialVersionUID
private static final long serialVersionUID = 42L
显示定义串行版本的UID值
3、有transient修饰符修饰的变量并不会被序列化
注意:本文归作者所有,未经作者允许,不得转载