前言
除了对关系型数据库的整合支持外,SpringBoot对非关系型数据库也提供了非常好的支持,比如,对Redis的支持。
Redis(Remote Dictionary Server,即远程字典服务)是一个高性能的key-value数据库,它是一种跨平台的非关系型数据库。Redis 通常被称为数据结构服务器,因为它的值(value)可以是字符串(String)、哈希(Hash)、列表(list)、集合(sets)和有序集合(sorted sets)等类型。
下面,我们来看一下SpringBoot与Redis要如何进行整合。
SpringBoot与非关系型数据库Redis的整合
(1)添加Spring Data Redis依赖启动器
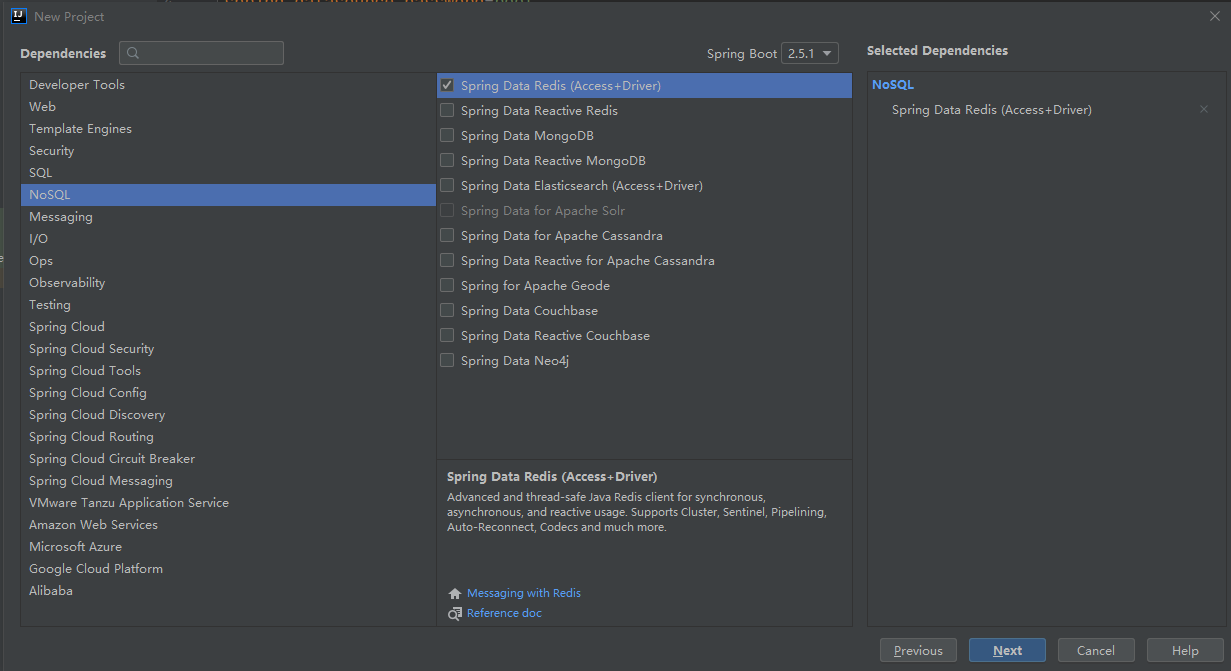
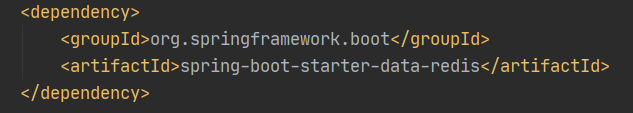
引入这个依赖器创建项目,在项目pom.xml文件会出现以下依赖:
(2)编写实体类
Person:
package com.hardy.springbootdataredis.domain;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisHash;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.index.Indexed;
/**
* @Author: HardyYao
* @Date: 2021/6/15
*/
@RedisHash("persons") // 指定操作实体类对象在Redis数据库中的存储空间
public class Person {
@Id // 标识实体类主键
private String id;
@Indexed // 标识对应属性在Redis数据库中生成二级索引
private String firstname;
@Indexed
private String lastname;
private Address address;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getFirstname() {
return firstname;
}
public void setFirstname(String firstname) {
this.firstname = firstname;
}
public String getLastname() {
return lastname;
}
public void setLastname(String lastname) {
this.lastname = lastname;
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"id='" + id + '\'' +
", firstname='" + firstname + '\'' +
", lastname='" + lastname + '\'' +
", address=" + address +
'}';
}
}Address:
package com.hardy.springbootdataredis.domain;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.index.Indexed;
/**
* @Author: HardyYao
* @Date: 2021/6/15
*/
public class Address {
@Indexed
private String city;
@Indexed
private String country;
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
public String getCountry() {
return country;
}
public void setCountry(String country) {
this.country = country;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Address{" +
"city='" + city + '\'' +
", country='" + country + '\'' +
'}';
}
}在上述两个实体类中,涉及了关于Redis数据库的数据操作的几个注解:
- @RedisHash("persons"):用于指定操作实体类对象在Redis数据库中的存储空间,此处表示针对Person实体类的数据操作都存储在Redis数据库中名为persons的存储空间下。
- @Id:用于标识实体类主键。在Redis数据库中会默认生成字符串形式的HashKey表示唯一的实体对象id,当然也可以在数据存储时手动指定id。
- @Indexed:用于标识对应属性在Redis数据库中生成二级索引。使用该注解后会在数据库中生成属性对应的二级索引,索引名称就是属性名,可以方便地进行数据查询。
(3)编写Repository接口
SpringBoot针对包括Redis在内的一些常用数据库提供了自动化配置,可以通过实现Repository接口简化对数据库中的数据进行增删查改的操作:
package com.hardy.springbootdataredis.repository;
import com.hardy.springbootdataredis.domain.Person;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Author: HardyYao
* @Date: 2021/6/15
*/
public interface PersonRepository extends CrudRepository<Person, String> {
List<Person> findByAddress_City(String City);
}注意:在操作Redis数据库时编写的Repository接口类需要继承最底层的CrudRepository接口,而不是继承JpaRepository(JpaRepository是SpringBoot整合JPA特有的)。当然,也可以在项目pom.xml文件中同时导入SpringBoot整合的JPA依赖和Redis依赖,这样就可以编写一个继承JpaRepository的接口的操作Redis数据库。
(4)Redis数据库连接配置
在项目的全局配置文件application.properties中添加Redis数据库的连接配置,示例代码如下:
# Redis服务器地址
spring.redis.host=127.0.0.1
# Redis服务器连接端口
spring.redis.port=6379
# Redis服务器连接密码(默认为空)
spring.redis.password=(5)编写单元测试方法
package com.hardy.springbootdataredis;
import com.hardy.springbootdataredis.domain.Address;
import com.hardy.springbootdataredis.domain.Person;
import com.hardy.springbootdataredis.repository.PersonRepository;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
class SpringbootdataRedisApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private PersonRepository repository;
@Test
public void savePerson() {
Person person = new Person();
person.setFirstname("张");
person.setLastname("三");
Address address = new Address();
address.setCity("北京");
address.setCountry("中国");
person.setAddress(address);
// 向Redis数据库添加数据
Person save = repository.save(person);
}
@Test
public void selectPerson() {
List<Person> list = repository.findByAddress_City("北京");
for (Person person : list) {
System.out.println(person);
}
}
}(6)整合测试
打开Redis客户端可视化管理工具,先连接本地Redis服务器:
连接成功后,可以看到原来本地Redis数据库中是没有数据的:

运行上文中编写好的两个测试方法,查看控制台打印结果:

为了验证save()方法确实把数据写入到本地Redis数据库中了,打开Redis客户端可视化管理工具,刷新一下数据,可以看到数据成功写入了:
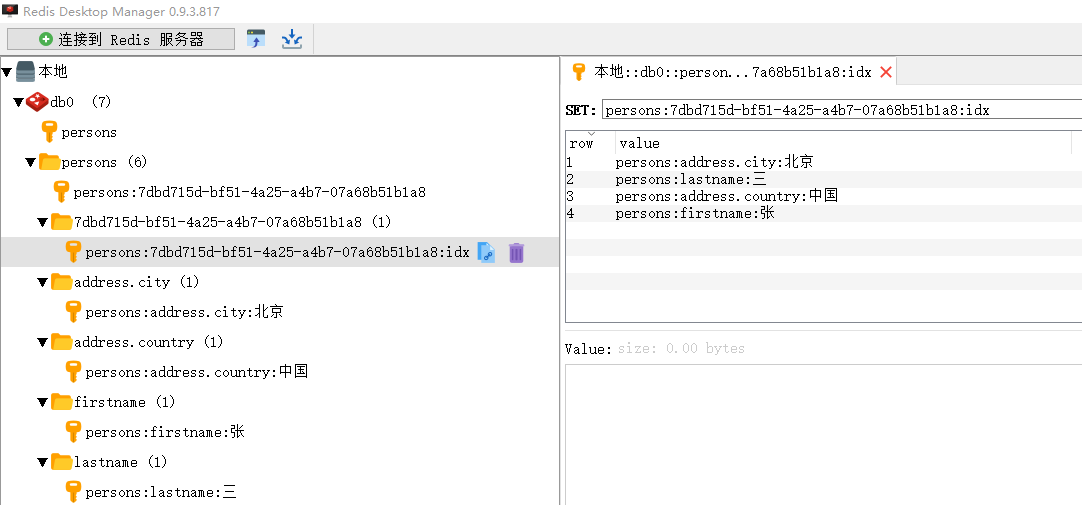
通过上图可知:执行save()方法添加的数据在Redis数据库中存储成功。另外,在数据库列表左侧还形成了一张类似address.city、firstname、lastname等二级索引,这些二级索引是前面创建Person类时在对应属性上添加@Indexed注解而生成的。同时,由于在Redis数据库中生成了对应属性的二级索引,所以可以通过二级索引来查询具体的数据信息,例如repository.findByAddress_City("北京")通过address.city索引查询索引值为北京的数据信息。如果没有设置对应属性的二级索引,那么通过属性索引查询的数据结果将为空。
注意:本文归作者所有,未经作者允许,不得转载